- +52 477 712 6000
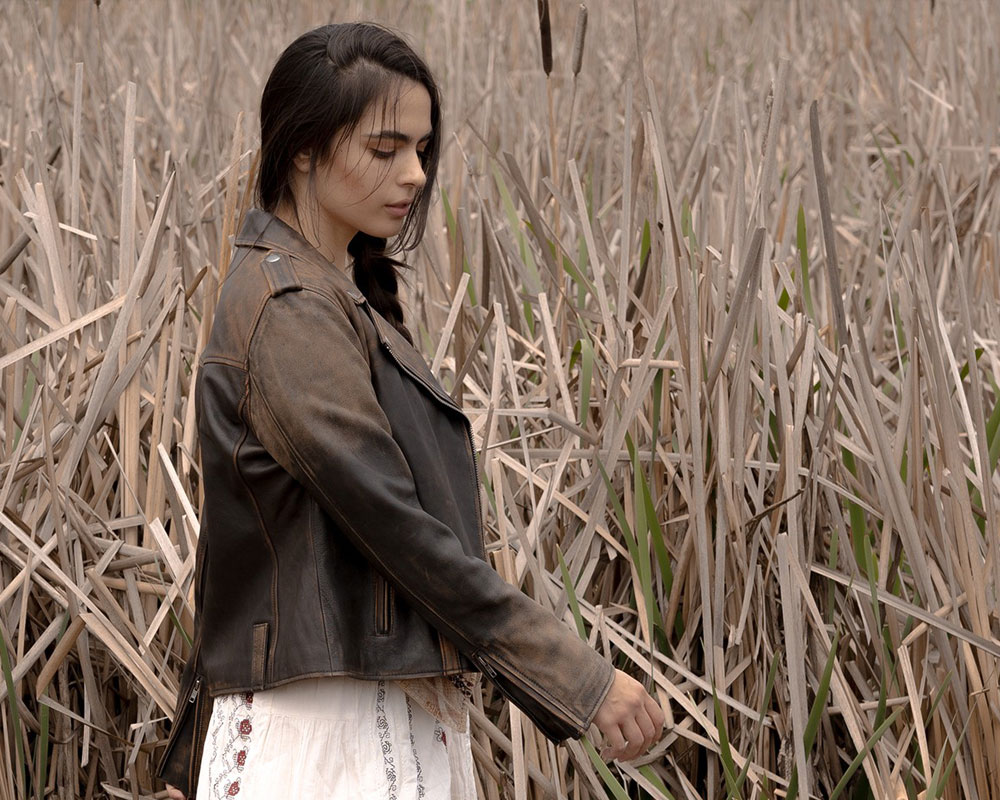

GENUINE LEATHER VS. FAKE: 5 SIMPLE TESTS TO TELL THE DIFFERENCE
Today we share with you the top ways to identify if your jacket is genuine leather or an imitation, based on industry practices and expert advice.
Over time, a genuine leather jacket is not only a symbol of elegance and durability, but also a long-term investment. However, with the growing supply of synthetic materials and imitation technologies, telling whether a leather item is real or fake can be a real challenge.
Today we share the main ways to identify if your jacket is made of genuine leather or imitation, based on industry practices and expert tips.

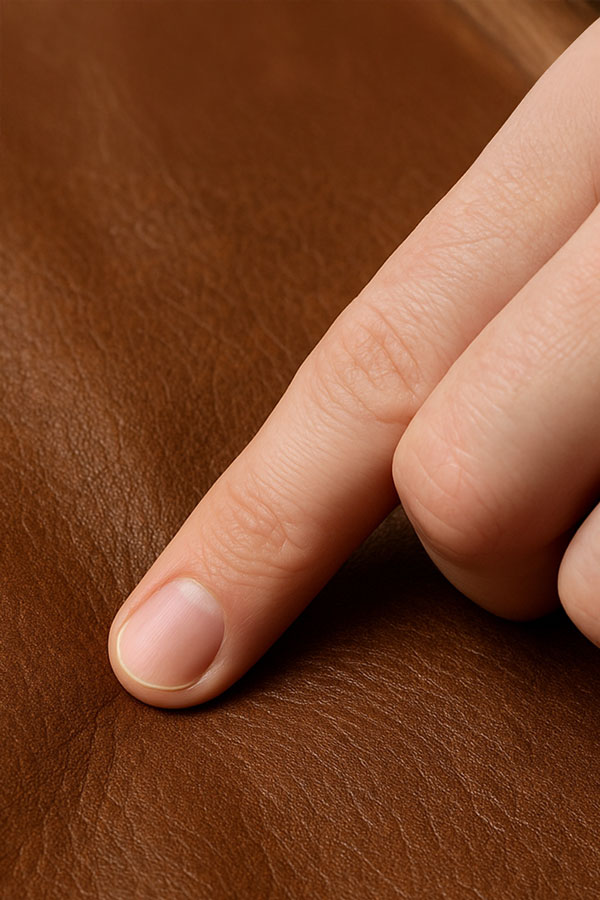
1. Touch: genuine leather is uneven and soft
Real leather has a natural texture, with slight imperfections—small pores, creases, or variations. When you touch it, it feels soft, warm, and flexible.
In contrast, synthetic leather often feels too uniform, plastic-like, or cold to the touch. Also, when pressed, real leather forms natural wrinkles, while synthetic material barely deforms or instantly returns to its original shape.
Expert Tip
Gently rub the surface of the jacket with your fingers or a cloth. Genuine leather usually feels warm and soft with a natural texture, reacting flexibly to pressure or contact. Synthetic materials tend to feel stiffer, colder, and may even squeak slightly when rubbed—producing an artificial, plastic-like sound. This subtle detail can help you distinguish between real and fake leather.
2. Smell: your nose won’t lie
The characteristic smell of leather is one of the most reliable ways to determine if it's real or fake.
Authentic leather has a distinctive, slightly woody or earthy scent—similar to oak—caused by the natural tanning process.
Faux leather, on the other hand, smells like plastic or chemical compounds.
3. Visual Aspect: natural pores and patterns
Look closely. Genuine leather shows irregular patterns: the pores vary in size and are not perfectly aligned.
Synthetic materials display highly uniform patterns, as they are industrially printed.
There’s usually a spot where you can see the leather’s edge and its internal composition. If you see threads or woven fabric inside, it’s synthetic leather (PU). If you see fine, fuzzy fibers, it’s likely tanned genuine leather.
According to the Leather Research Laboratory at the University of Cincinnati, a microscope reveals that natural leather fibers form 3D networks, while synthetics appear flat or artificially woven.
4. Label and certifications.
Some counterfeit leather products—especially from informal markets—try to include misleading tags claiming they’re made of real leather.
When inspecting a leather garment, check the label to see if it mentions real leather. If you see terms like “synthetic” or “polyester,” it’s not genuine leather. While tags can be faked, they’re still a good starting point.
Look for labels that say:
- “100% leather”
- “Genuine leather”
- “Full-grain leather”
- “Top-grain leather”
Beware: Terms like “PU leather,” “vegan leather,” or “synthetic leather” clearly indicate artificial materials.
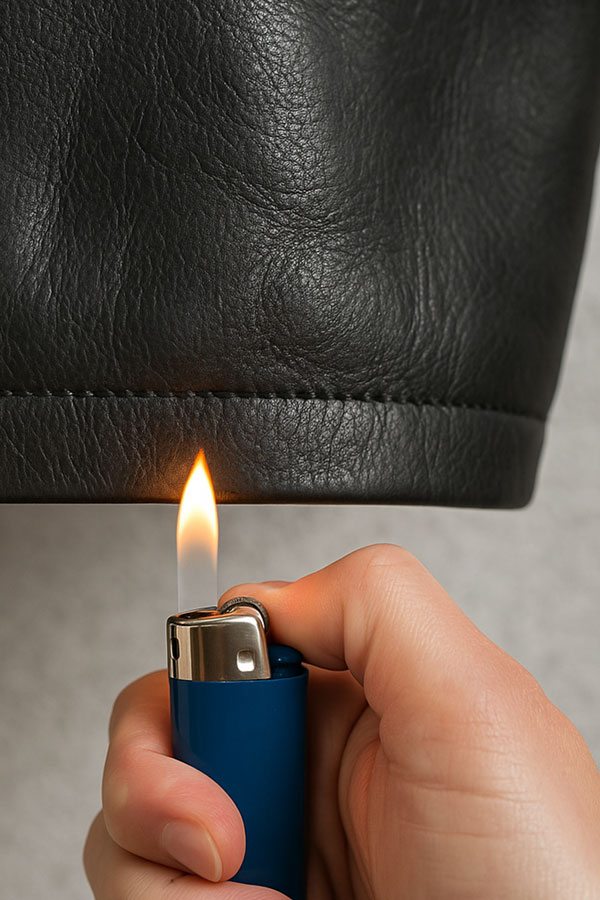


5. Fire Test
The fire or heat test is the most definitive method—but also the most aggressive.
It involves applying a heat source or flame for 5 to 10 seconds. Real leather may become slightly stiff and release a smell similar to burnt hair—but it won’t ignite.
In contrast, synthetic leather will deform, melt, and possibly catch fire. It also emits a strong burnt plastic odor when exposed to flame.
Warning: This test is not recommended on new or valuable items, as it can damage even genuine leather products.